Qedma’s Next-Generation Quantum Error-Mitigation Software Available as IBM Qiskit Function

Insider Brief:
- Qedma has introduced its Quantum Error Suppression and Error Mitigation (QESEM) solution as part of IBM’s Qiskit Functions.
- QESEM combines quantum error suppression, which reduces hardware-level errors, and quantum error mitigation, which eliminates error impacts without extra qubits, providing a resource-efficient solution to improve quantum computation reliability.
- The software is designed for high-accuracy execution of utility-scale quantum circuits, with application-agnostic performance, user-friendly API integration, and QPU-time estimation to optimize resource management.
- Qedma’s roadmap includes further development of QESEM to reduce qubit overhead and enhance error correction, aiming to accelerate the timeline for achieving practical quantum advantage and enabling quantum computing’s commercial viability.
PRESS RELEASE Tel Aviv, Israel, September 16th, 2024 — Qedma, a leading quantum computing software company, announced the availability of its Quantum Error Suppression and Error Mitigation (QESEM) solution as an IBM’s Qiskit Function, supplying a crucial component in the quantum technology stack to enable quantum algorithms to achieve high accuracy at large scales.
Qedma is focused on delivering value to customers and clients eager to explore and exploit quantum computing for their unique challenges. Reflecting on the collaboration, Prof. Netanel Lindner, Qedma’s CTO, said, “Working with IBM has been an amazing experience because of the large, engaged community they’ve built. This community includes researchers who are pushing the boundaries of quantum computing, which aligns perfectly with our goals at Qedma.”
Delivering a Qiskit Function for the Quantum Computing Stack
Qedma’s QESEM technology is now available through IBM’s new Qiskit Functions to run on IBM’s utility scale quantum devices, including Eagle and Heron processors. Qedma’s team is ensuring that their software solutions seamlessly complement IBM’s hardware advancements, driving towards a vision of quantum advantage.
“Error mitigation will be an essential tool for reaching quantum advantage. Capabilities from partners like Qedma integrated in Qiskit Functions allow users to seamlessly take advantage of these techniques to improve the accuracy of executing utility-scale circuits and beyond. These advances pave the way for unlocking value from near-term quantum computation, and I invite the quantum community to begin to utilize these powerful tools,” said Jay Gambetta, IBM Fellow and Vice President, IBM Quantum.
Addressing Key Challenges in Quantum Computing: Unlocking Scale and Reliability
The current state of quantum computing faces two significant challenges: scaling the number of qubits and managing errors that compromise computational reliability. Traditional quantum error correction methods use many additional qubits and gates to detect and correct errors, making them very resource intensive. Qedma’s QESEM software addresses these challenges by combining quantum error suppression, which reduces errors at the hardware level, with quantum error mitigation, which eliminates the impact of errors without requiring extra qubits.
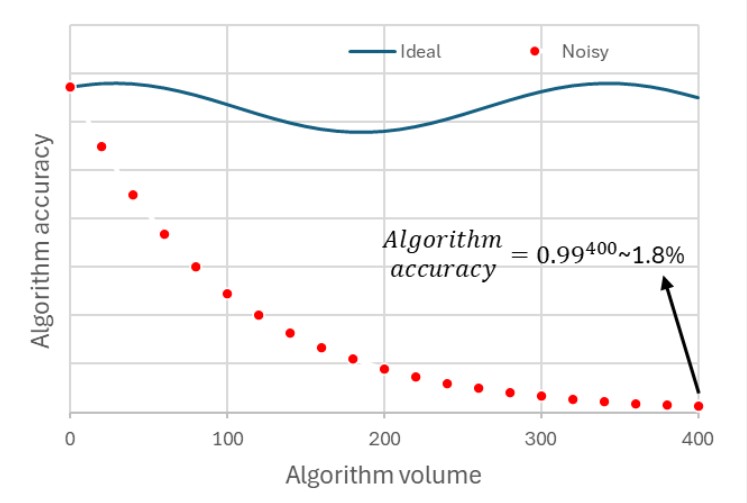
QESEM’s efficient, dual approach offers a practical trade-off between resources and time. Instead of the current qubit and gate-overhead techniques envisioned as needed to achieve eventual error correction, QESEM’s error suppression and mitigation techniques utilize a manageable increase in quantum computation time—a more readily available resource today—to provide a solution to current challenges. As Dr. Asif Sinay, CEO and co-founder of Qedma, notes, “Errors are at the top of the list of challenges in quantum computing. No matter how many qubits are in a quantum processor, if the computation is not reliable, it doesn’t matter. Our solution focuses on real-time error suppression and mitigation, enabling us to accelerate the quantum advantage timeline.”
Key Features of QESEM: A Comprehensive User-Centric Solution for Reliable Quantum Computing
- Unbiased Error Mitigation: QESEM offers powerful unbiased error mitigation, ensuring high levels of accuracy based on the user’s QPU time allocation.
- Application-Agnostic Performance: QESEM is designed to provide high-accuracy results for generic quantum circuits and observables while optimizing performance with advanced circuit compilation.
- Error Reduction at Scale: By combining error suppression at the hardware level and error mitigation at the circuit level, QESEM supports high-accuracy execution of utility-scale quantum circuits.
- User-Friendly Interface and QPU-Time Estimation: QESEM’s intuitive interface features easy API integration and QPU-time estimation to help users manage resources efficiently.
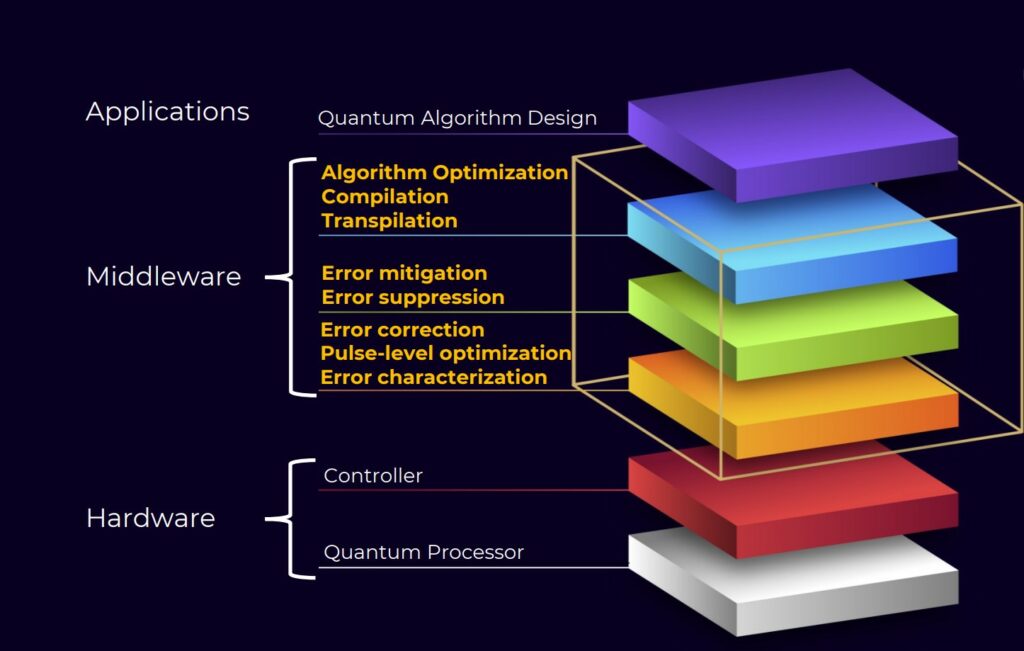
A Roadmap to Quantum Advantage
Qedma has a clear strategy for scaling QESEM to support larger quantum volumes and further hardware modalities. The company is actively working on the next version of QESEM, which aims to reduce qubit overhead in error correction. This next phase will enable the reliable execution of error-corrected circuits, boosting the effectiveness of error correction and accelerating its practical use.
Qedma’s mission extends beyond technological details; it’s about accelerating the timeline to make quantum advantage commercially viable and accessible, transforming industries and addressing critical societal challenges.
Shaping the Future of Quantum Computing
Qedma is redefining the landscape of quantum computing by tackling the field’s most significant challenges head-on: error management. With QESEM, Qedma is empowering researchers, enterprise, and developers to unlock the potential of quantum algorithms and advance toward quantum advantage. Backed by a world-class team and a clear vision for the future, Qedma is well-positioned to shape the future of quantum computing.
Meet the Qedma Team

Qedma’s team, composed of experts across quantum computing and quantum information, is uniquely positioned to deliver on the company’s ambitious vision. Dr. Asif Sinay, CEO of Qedma, reflects on their journey, stating, “Skepticism was always part of my life. People would tell us, ‘It’s impossible.’ But when you believe in what you’re doing, have results to support it, and a strong team, then the sky’s the limit.”
Dr. Asif Sinay, CEO & Co-Founder:
A former researcher at Magic Leap and a graduate of the prestigious Talpiot program, Dr. Sinay is determined to build an operating system for quantum computers that can change the face of computing. With advanced degrees in physics and experience in both industry and academia, Dr. Sinay’s leadership has been instrumental in developing Qedma’s strategy and vision.
Prof. Dorit Aharonov, CSO & Co-Founder:
A world-renowned quantum theorist and co-founder of Qedma, Prof. Aharonov’s proof of the fault tolerance theorem has laid the foundation for the field of quantum error correction. Her work in noise reduction, quantum verification, and error mitigation protocols is central to both the development of Qedma’s core technology and the broader advancement of quantum computing.
Prof. Netanel Lindner, CTO & Co-Founder:
With deep expertise in quantum many-body systems, photonic and topological quantum computing, Prof. Lindner leads Qedma’s technological development. His pioneering work in non-equilibrium topological quantum matter and related fields has played a crucial role in advancing the company’s innovative QESEM product.
About Qedma:
Qedma is an innovative quantum computing software company focused on addressing the most significant challenges in the field through its advanced Quantum Error Suppression and Error Mitigation (QESEM) solutions. Through hardware-agnostic and application-agnostic middleware, Qedma is enabling quantum algorithms to achieve unprecedented accuracy and reliability. The company’s interdisciplinary team, composed of experts in theoretical and applied quantum computing, alongside exceptional software engineers, is dedicated to making quantum advantage a practical reality. Qedma is developing the full-stack quantum software necessary to unlock the full potential of quantum computing.
