Oxford Ionics Wins Award From Germany to Build Portable Quantum Computer
Insider Brief
- Oxford Ionics won a contract to build a state-of-the-art portable quantum computer for the Cyberagentur, Germany’s Agency for Innovation in Cybersecurity.
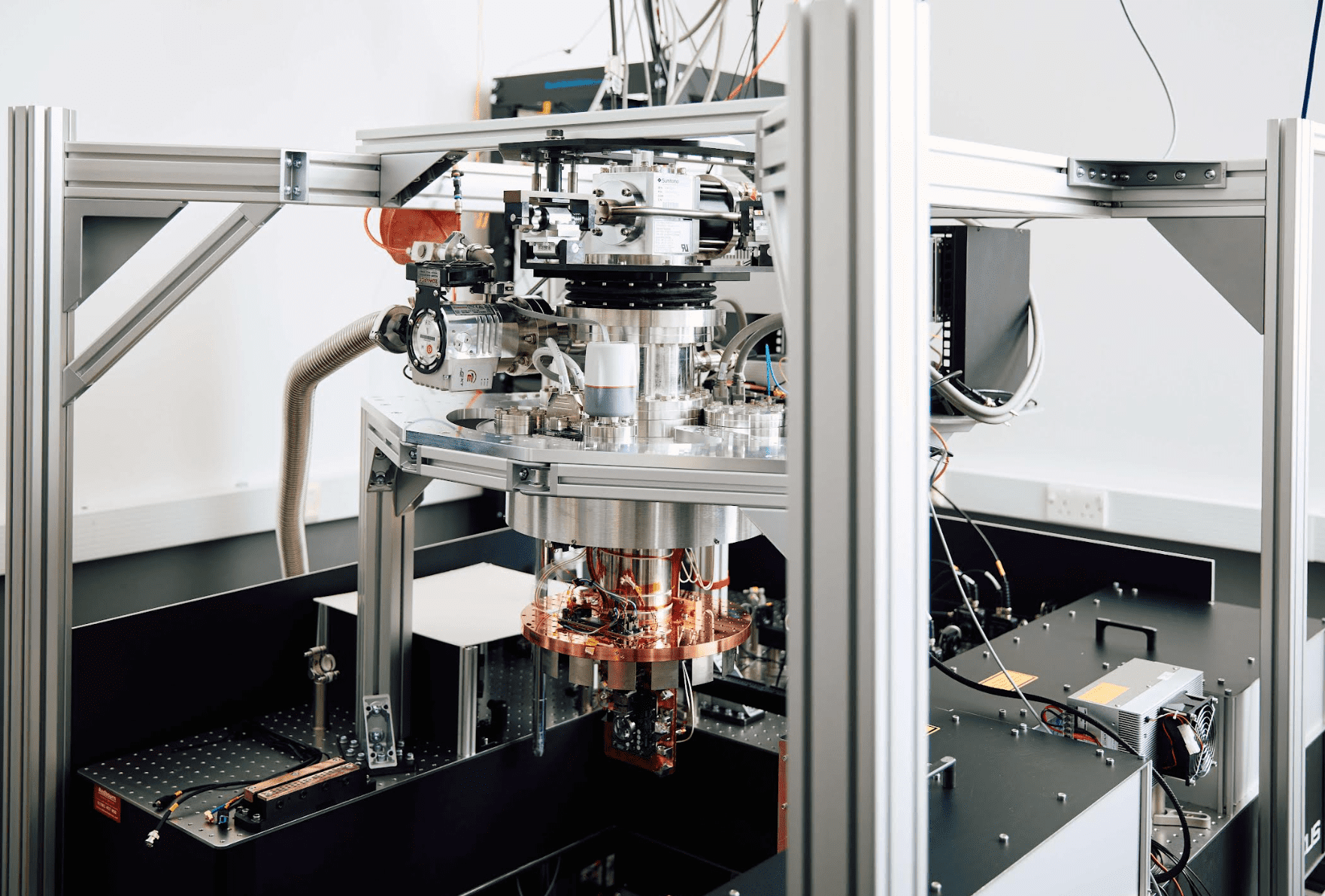
- The mobile quantum system, called MinIon, is mobile variant of Oxford Ionics’ line of quantum computers and designed to be compact and robust.
- Cyberagentur will leverage MinIon for applications in national security and defense.
PRESS RELEASE — Oxford Ionics, a world leader in trapped-ion quantum computing, announced that it has won a contract to build a state-of-the-art portable quantum computer for the Cyberagentur, Germany’s Agency for Innovation in Cybersecurity.
Founded by the German Federal Government, the Cyberagentur aims to progress research and innovation in the field of cybersecurity to promote the country’s internal and external security. The Cyberagentur will use Oxford Ionics’ portable quantum computer, called MinIon, for application development in national security and defence.
Quantum computers are of particular interest for governments, as they can prove integral to national security and digital sovereignty. Government bodies around the world are already exploring different applications of quantum computing, from enhanced computing power to cryptography. The Cyberagentur is specifically focused on applying quantum computing to ‘mobile defence’, meaning it can leverage a compact, lightweight, and energy-efficient mobile quantum computer for security and defence scenarios. These smaller systems are easily deployed, transported, and upgraded in the field – giving nation-states a crucial advantage.
Oxford Ionics is uniquely positioned in the industry to deliver a mobile quantum computer. The company has developed a proprietary technology called ‘Electronic Qubit Control’ – meaning it uses electronics, not lasers, to control its qubits. This inherently robust technology can then be integrated onto a standard, thumbnail-sized chip produced in today’s semiconductor fabrication facilities. Through this unique approach, Oxford Ionics’ quantum computers can deliver powerful computational capabilities within an industry-leading small physical footprint where that is important for the particular needs of an organisation.
MinIon will be the sixth quantum computer delivered by Oxford Ionics, following a contract won earlier this year with the UK’s National Quantum Computing Centre (NQCC). As an R&D partner of Oxford Ionics, Infineon AG will contribute its expertise in microfabrication of highly reliable, large-scale ion trap chips. The two companies will work together to develop increasingly powerful quantum processor units (QPUs) that leverage Oxford Ionics’ scalable manufacturing and world-leading position in qubit quality. This quality was recently demonstrated with Oxford Ionics’ world-record performance in single- and two-qubit gate fidelity and quantum state preparation and measurement (SPAM).
Dr Roman Bansen, Head of Quantum Technologies at the Cyberagentur, commented: “Mobile systems are particularly important for security and defence scenarios, as they can operate independently of a data connection to stationary data centres. Especially in crises or defence situations, this is essential. At the same time, mobile quantum computers also potentially offer considerable advantages for civilian applications.”
Dr Chris Ballance, Oxford Ionics co-founder and CEO, commented: “We are thrilled to be delivering the first mobile variant of our product line to the Cyberagentur. Since our inception, we have viewed the challenge of building powerful quantum computers as an engineering project – not a science project. This approach has yielded both the highest performing chips in the world and a robust technology that can deliver industry-leading performance within a small physical footprint based on customer needs. MinIon represents the first of these small systems, which is uniquely engineered to suit the dynamic, fast-paced nature of national security and defence.”
