QCentroid Joins Q-CTRL’s Network of Fire Opal Partners, Expanding Access to Enterprise-Grade Quantum Solutions
Insider Brief:
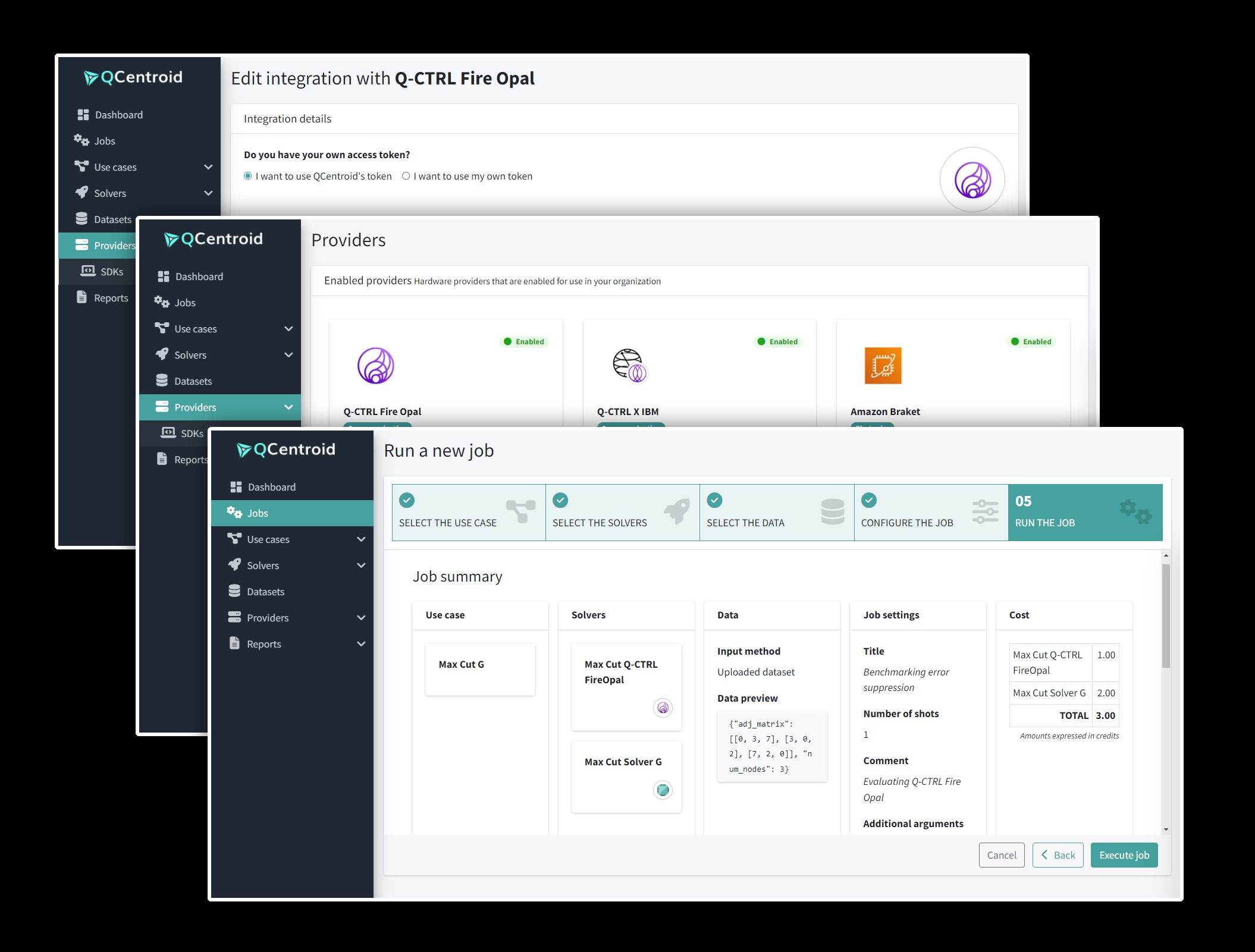
- Fire Opal’s integration with QCentroid offers developers a user-friendly platform with no-code and API tools to test and deploy quantum algorithms.
- AI-driven error suppression in Fire Opal may improve the success of quantum algorithms on real hardware by up to 1000x, enabling users to scale complex quantum problems and abstract hardware complexities.
- QCentroid users gain access to Fire Opal’s advanced solvers, including the record-setting MaxCut optimization problem, providing powerful tools for a range of applications like risk analysis and chemistry simulations.
- Monitoring and visualization tools on QCentroid allow users to evaluate Fire Opal’s impact on execution time, cost, and performance for enterprise-grade quantum solutions.
PRESS RELEASE — Earlier this year, Q-CTRL shared exciting news about Fire Opal’s integration with some of the industry’s top platforms for quantum application developers. In a recent post, Q-CTRL announced that QCentroid would be joining their growing network of Fire Opal partners.
Fire Opal and QCentroid Integration Provides Scalable Solutions
As the quantum industry progresses towards the use of enterprise applications, particularly those that may one day be driven by utility-scale quantum hardware, the integration between Fire Opal and QCentroid offers developers an easy-to-use platform to test algorithms and deploy solutions. Fire Opal, now accessible through the QCentroid Platform, assists in eliminating potential barriers to quantum adoption by offering no-code and API tools. The platform’s comprehensive monitoring tools provide real-time insights, so that users may also be able to optimize algorithm performance and manage costs efficiently.
For developers working on a range of problems—from risk analysis and collateral optimization to EV location placement and chemistry simulations—QCentroid users now have the added benefit of Fire Opal’s AI-driven error suppression. As noted in the post, this technology could improve algorithm success rates on real hardware by up to 1000x, helping users scale complex quantum problems while abstracting hardware complexities. Additionally, the platform’s extensive library of solvers includes the MaxCut optimization problem, which, according to the post, recently set records for the one of the largest and most complex MaxCut problems solved on gate-model quantum computers.
Fire Opal at the Core of Quantum Applications
According to the Q-CTRL team, Fire Opal was designed to simplify the complexities quantum computing by abstracting hardware-level execution and focusing on results. The software addresses challenges such as error suppression and cost-efficient scaling, which are cited as key concerns for quantum application developers. Through the new integration, QCentroid users can directly access Fire Opal’s core functionality for error suppression directly within the platform. This provides users with high-performance results on real quantum hardware without the need for extra configuration.
As Heather West, an analyst at IDC, puts it, “Fire Opal is delivering frictionless quantum software.” With QCentroid’s intuitive interface and pre-built solvers, friction may be even further reduced for developers, researchers, and businesses through access to smoother development workflows. By selecting the Fire Opal provider, users can execute complex quantum tasks, from circuit compilation to error management, without manual intervention.
Benchmarking Performance and Cost Efficiency
QCentroid’s monitoring and visualization tools make it easy for users to evaluate how much Fire Opal improves execution time, cost, and overall algorithm performance. The clear results demonstrate Fire Opal’s ability to enhance efficiency, enabling users to achieve enterprise-grade quantum solutions more effectively.
Quantum Optimization for Everyone
As quantum technology becomes more widely adopted, partnerships like that between QCentroid and Q-CTRL are essential for making quantum computing more accessible and practical. By leveraging the strengths of both platforms, this collaboration paves the way for innovation and discovery, offering businesses, researchers, and developers the tools they need to unlock new possibilities in quantum computing.
