Researchers Say IP Trends Show Rapid-Growing Quantum Ecosystem is ‘Co-Evolving’, Entering Maturity Stage

Insider Brief
- Quantum computing appears to be undergoing rapid acceleration, patent accumulation shows.
- This surge is marked by increasing interactions among various topics within the quantum computing field.
- The researchers suggest that this co-evolutionary pattern offers insights into the current quantum ecosystem, as well as implications for people participating in this complex, fast-changing field.
The quantum technology industry is often referred to as emerging tech, or frontier tech. It may, however, be far more mature than many realize, according to a study of intellectual property trends published in the Journal of the Knowledge Economy.
According to the researchers — Mario Coccia, CNR – National Research Council of Italy, IRCRES and Saeed Roshani, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iraq — quantum computing appears to be undergoing rapid acceleration, as seen in the accumulation of patents in key research areas.
This technological surge is marked by increasing interactions among various topics within the quantum computing field, which has, in turn, created a dense network of interrelated research and technological development. While this growth may seem sudden and highly complex — and those are both true — the researchers suggest that the evolution of the quantum ecosystem is totally incomprehensible.
In the study, the researchers point out that most of the growth happened in the last decade, however, they report a somewhat logical evolution because quantum computing technology grew and changed along with internal processes. The type of evolution experienced by quantum encourages a lot of interaction between different research areas and creates a dense network of interconnected fields and technologies, This could, then, helps us better understand how science and technology develop over time.
They write: “The findings reveal that the evolutionary dynamics of quantum computing co-evolves with endogenous processes that support high interactions with manifold topics within the network, increasing the extension and density of connections with inter-related research fields and technologies. These observed dynamics enrich our theoretical understanding of how scientific and technological fields evolve, especially the role of vital topics in fostering interconnections and cumulative knowledge over time.”
To conduct the study, the researchers used the Derwent Innovation Index (DII) from the Web of Science database to collect patent data. This dataset, updated weekly, includes over 14.3 million inventions from nearly 60 global patent-issuing authorities. The study employed a logistic model to identify different stages in the technology life cycle and an entity-linking method to uncover central themes in quantum computing research.
Emerging or Maturing?
One of the study’s key findings is that quantum computing technology has reached a mature phase.
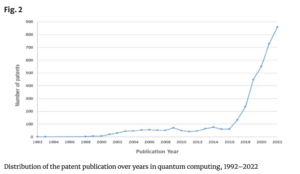
The maturity stage is marked by a sharp increase in the number of patents filed since 2016, which underscores the significant progress and development in the field. Specifically, important areas of research, like qubits, quantum gates, quantum information and quantum dots, have grown rapidly. These areas are crucial to how quantum computing technology advances and highlight its evolution and importance, the researchers report.
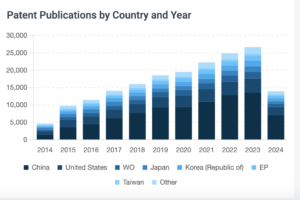
Similarly, The Quantum Insider’s Intelligence Platform shows a rapid growth of quantum patents with an inflection point in the mid 2010s. The platform allows dives into specific quantum technologies and, on a cursory look, closely replicates the researchers’ findings to this growth across several varieties of quantum technologies. Interestingly, the platform shows that by the first half of 2024, the output of quantum-related patents has nearly matched the output of that pivotal 2016 period.
While it’s hard to predict future trends based on current data, the possibility exists that rather than a maturing, this sudden growth could be followed by an even more accelerated period of innovation if quantum technologies reach a more mainstream acceptance, which has not happened as yet.
Creating a Quantum Roadmap
The findings can be used to create a practical roadmap for understanding the future development of quantum computing, according to the researchers. The roadmap could the following elements:
Identifying Key Development Stages: Recognizing the three stages of quantum computing evolution—emerging, growth, and maturity—helps stakeholders understand the current phase of the technology and anticipate future trends.
Focus on Dominant Topics: Areas such as qubits, quantum gates, quantum information, and quantum dots are growing rapidly. Concentrating research and development efforts on these topics can drive further technological advancements.
Strategic Resource Allocation: By understanding which topics are emerging, dominant, declining, or saturated, stakeholders can allocate resources effectively to maximize impact and foster innovation.
Encouraging Interactions and Collaborations: The study highlights the importance of interactions among different research areas. Promoting collaboration between various fields can enhance technological development and create a more integrated research network.
Monitoring Patent Filings: Keeping track of patent trends can provide insights into the technological progress and help predict future developments. A surge in patent filings can indicate significant advancements and emerging opportunities.
Adapting to Evolving Dynamics: Understanding the co-evolutionary nature of quantum computing technologies can help stakeholders adapt to changing dynamics and leverage new opportunities in the market.
Strategic Implications
The researchers suggest that the study offers implications for various stakeholders, including policymakers, R&D managers and technology analysts that could help them navigate the rapid growth of quantum. Understanding the evolutionary dynamics and co-evolutionary patterns in quantum computing can inform strategic decisions and drive innovation effectively, they write.
Strategic Resource Allocation: R&D investments are crucial for driving scientific and technological development. By identifying dominant and emerging topics, stakeholders can allocate resources more effectively to areas with the highest potential for impact.
Collaborative Opportunities: The study highlights the co-evolutionary dynamics and network structures of quantum computing topics, revealing opportunities for cross-fertilization of ideas and projects. Strategic collaborations can accelerate technological advancements and foster innovation.
Technology Transfer and Market Opportunities: Insights into the co-evolutionary nature of quantum computing technologies can help identify emerging market opportunities. Companies can leverage these insights to develop new products and services that meet evolving market demands.
Competitiveness and Market Positioning: By analyzing the morphological changes in the network of patent topics, industrial players can assess their competitiveness and market positioning within the quantum computing ecosystem. This information is vital for developing strategies to maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
Implications for Stakeholders
The insights from this study are valuable for policymakers, R&D managers, and technology analysts. Understanding the evolutionary dynamics and co-evolutionary patterns in quantum computing can inform strategic decisions and drive innovation effectively.
Strategic Resource Allocation: By identifying dominant and emerging topics, stakeholders can allocate resources more effectively to areas with the highest potential impact.
The researchers write: “Funding directed to cutting-edge research encourages collaboration and strategic alliances among firms to design and foster the development of breakthrough innovations. For instance, by identifying “Quantum Information” as a dominant technology with a high degree of centrality, R&D managers can prioritize funding for projects related to quantum information processing, enabling advancements in quantum algorithms and cryptographic systems having a lot of practical applications.”
Collaborative Opportunities: The study highlights potential opportunities for cross-fertilization of ideas and projects, accelerating technological advancements.
“Interconnected technologies offer a fertile ground for collaborative initiatives among researchers, academic institutions, and industry players,” the researchers write. “Partnerships of firms and academic institutions across different fields can lead to the emergence of disruptive innovations and accelerate the technology’s commercialization.”
Market Opportunities: Insights into the co-evolutionary nature of quantum computing technologies help identify emerging market opportunities.
The researchers write: “Identifying technologies that are transitioning from the growth phase to the maturity phase can help stakeholders to anticipate market demand and prepare for technology transfer of innovations in markets.”
Competitiveness and Market Positioning: Analyzing the changes in the network of patent topics allows industrial players to assess their competitiveness within the quantum computing ecosystem.
The paper covers a range of topics important to quantum and goes into more detail than this summary — you can review it here.